ISSUE1677
- Mark Abramowicz, M.D., President has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
- Jean-Marie Pflomm, Pharm.D., Editor in Chief has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
- Brinda M. Shah, Pharm.D., Consulting Editor has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
- Michael Viscusi, Pharm.D., Associate Editor has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
- Review the efficacy and safety of vilobelimab (Gohibic) for treatment of COVID-19 in hospitalized adults receiving mechanical ventilation or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
The investigational anti-complement component 5a (C5a) antibody vilobelimab (Gohibic – InflaRx) has been granted an FDA Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for IV treatment of hospitalized adults with COVID-19 beginning within 48 hours after invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is started. Vilobelimab is the first anti-C5a antibody to become available in the US.1

STANDARD TREATMENT ― The NIH recommends that adults with COVID-19 who require IMV or ECMO receive the corticosteroid dexamethasone and either the oral Janus kinase inhibitor baricitinib (Olumiant) or the IV interleukin-6 receptor antagonist tocilizumab (Actemra). Baricitinib and tocilizumab are FDA-approved for treatment of hospitalized adults with COVID-19; they have decreased mortality when used with dexamethasone in critically ill patients, but data on their efficacy in patients requiring IMV or ECMO are limited.2-5 The IV antiviral drug remdesivir (Veklury) is also FDA-approved for inpatient use, but it has not had a survival benefit in patients already receiving IMV or ECMO.2,6
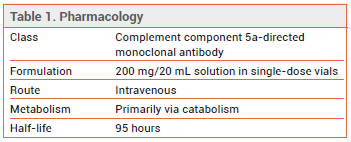
MECHANISM OF ACTION ― Activation of the complement system causes systemic inflammation and thrombosis and has been associated with poor outcomes in COVID-19. Vilobelimab is a chimeric human/murine monoclonal antibody that targets C5a, preventing it from binding to the C5a receptor.7
CLINICAL STUDIES ― Issuance of the EUA was based on the results of a double-blind trial (PANAMO) in 368 adults with COVID-19 who had begun IMV or ECMO therapy ≤48 hours previously. Patients were randomized to receive up to 6 doses of vilobelimab or placebo in addition to standard treatment; 97% of patients also received a corticosteroid such as dexamethasone.
The primary endpoint, all-cause mortality at day 28 adjusted for age and treatment site, occurred less often with vilobelimab than with placebo (32% vs 42%), but the difference was not statistically significant. In a prespecified sensitivity analysis that adjusted for age (but not treatment site) and used multiple imputation for missing data, the difference between the two groups was statistically significant (absolute risk reduction 11.2% [95% CI 1.4%-21.0%] NNT 8.9 [95% CI 4.8-71.4]). Similar results were observed at day 60.8,9
ADVERSE EFFECTS ― Serious infections have occurred with use of vilobelimab. In PANAMO, nonfatal pneumonia and sepsis occurred more often with the active drug than with placebo. Other adverse effects that occurred more often with vilobelimab included delirium, pulmonary embolism, hypertension, pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum, thrombocytopenia, and supraventricular tachycardia. Hypersensitivity reactions have been reported.8
PREGNANCY ― There are no adequate human data on use of vilobelimab during pregnancy. In pregnant cynomolgus monkeys, high doses of the drug did not cause adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.8
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ― The recommended dosage of vilobelimab is 800 mg given by IV infusion over 30-60 minutes up to 6 times (on days 1, 2, 4, 8, 15, and 22) while the patient remains hospitalized.
CONCLUSION ― The investigational IV anti-complement component 5a antibody vilobelimab (Gohibic) is available under an FDA Emergency Use Authorization for treatment of COVID-19 in hospitalized adults who recently began invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) therapy. Addition of vilobelimab to a corticosteroid such as dexamethasone appears to decrease mortality in such patients, but the data are mixed and more trials would be welcome. How vilobelimab compares to baricitinib (Olumiant) and tocilizumab (Actemra), which are recommended by the NIH for treatment of patients with COVID-19 who require IMV or ECMO, remains to be determined.
- FDA. FDA authorizes Gohibic (vilobelimab) injection for the treatment of COVID-19. April 4, 2023. Available at: https://bit.ly/3olWkgT. Accessed May 11, 2023.
- NIH. COVID-19 treatment guidelines. Therapeutic management of hospitalized adults with COVID-19. April 20, 2022. Available at: https://bit.ly/3DfsFsJ. Accessed May 11, 2023.
- X Zhang et al. The efficacy and safety of Janus kinase inhibitors for patients with COVID-19: a living systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Med (Lausanne) 2022; 8:800492. doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.800492
- COVID-19 update: Tocilizumab (Actemra) FDA-approved for treatment of COVID-19. Med Lett Drugs Ther 2023; 65:e9.
- REMAP CAP Investigators. Interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in critically ill patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med 2021; 384:1491. doi:10.1056/nejmoa2100433
- WHO Solidarity Trial Consortium. Remdesivir and three other drugs for hospitalised patients with COVID-19: final results of the WHO Solidarity randomised trial and updated meta-analyses. Lancet 2022; 399:1941. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(22)00519-0
- B Afzali et al. The state of complement in COVID-19. Nat Rev Immunol 2022; 22:77. doi:10.1038/s41577-021-00665-1
- FDA. Fact sheet for health care providers: Emergency Use Authorization for Gohibic. April 2023. Available at: https://bit.ly/3MPBukj. Accessed May 11, 2023.
- APJ Vlaar et al. Anti-C5a antibody (vilobelimab) therapy for critically ill, invasively mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19 (PANAMO): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir Med 2022; 10:1137. doi:10.1016/s2213-2600(22)00297-1