ISSUE1334
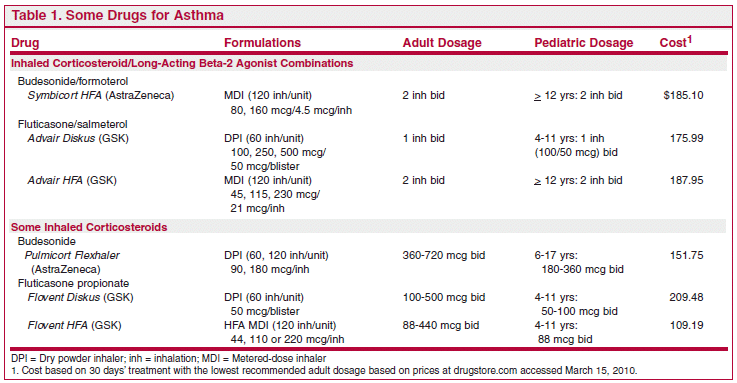
A little more than a year ago, The Medical Letter reported the results of an FDA meta-analysis which found that use of a long-acting beta-2 agonist (LABA) such as salmeterol (Severent) or formoterol (Foradil) in patients with asthma was associated with an increased risk of a composite endpoint of asthma-related death, intubation or hospitalization; the highest risk was in children 4-11 years old.There was no significant increase in risk when a long-acting beta-2 agonist was used with an inhaled corticosteroid.The Medical Letter recommended that long-acting beta-2 agonists should not be used as monotherapy for asthma, especially in children, and that long-acting beta-2 agonists should be used for asthma only in combination with an inhaled corticosteroid, preferably in a fixed-dose combination in the same inhaler.1
Now the FDA has issued new Safe Use Requirements2 and labeling requirements for long-acting beta-2 agonists that include the following: “Stop use of the LABA, if possible, once asthma control is achieved and maintain the use of an asthma-controller medication such as an inhaled corticosteroid.”3
It has not been determined that patients taking a long-acting beta-2 agonist in a fixed-dose combination with an inhaled corticosteroid have an increased risk of death or that stopping long-acting beta-2 agonists in such patients will improve long-term outcomes. A controlled clinical trial of these new requirements would be welcome.
1. Long-acting beta-2 agonists in asthma. Med Lett Drugs Ther 2009; 51:1.
